System Redesign
BUSINESS PROCESS REENGINEERING
Business Process Reengineering is the radical redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in productivity, cycle times, quality, enhance speed, cost reduction, employee and customer satisfaction. Companies start by assessing what work needs to be done to deliver customer value. It involves eliminating unnecessary and inefficient aspects of the workflow or aspects that add little value.
BPR is typically pursued to improve processes, increase productivity, reduce costs, improve customer service, and provide a competitive advantage. Continuous process improvement (CPI) is similar to BPR in that the objective is to reduce cost, improve productivity, or improve some other aspect of business operations.
The concept of business processes – interrelated activities aiming at creating a value added output to a customer – is the basic underlying idea of BPR. These processes are characterized by a number of attributes: Process ownership, customer focus, value adding, and cross-functionality.
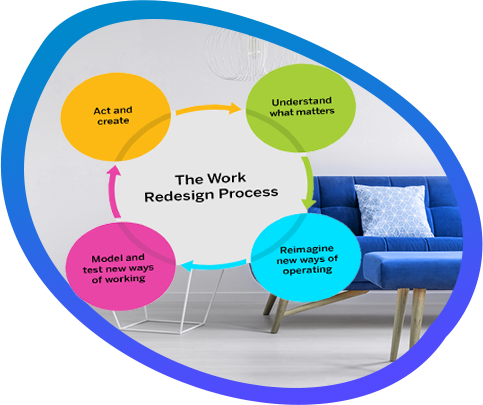
THE ROLE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Information technology (IT) has historically played an important role in the reengineering concept. It is regarded by some as a major enabler for new forms of working and collaborating within an organization and across organizational borders.
BPR literature identified several so called disruptive technologies that were supposed to challenge traditional wisdom about how work should be performed.
• Shared databases, making information available at many places
• Expert systems, allowing generalists to perform specialist tasks
• Telecommunication networks, allowing organizations to be centralized and decentralized at the same time
• Decision-support tools, allowing decision-making to be a part of everybody's job
• Wireless data communication and portable computers, allowing field personnel to work office independent
• Interactive videodisk, to get in immediate contact with potential buyers
• Automatic identification and tracking, allowing things to tell where they are, instead of requiring to be found
• High performance computing, allowing on-the-fly planning and revisioning
TEAM COMPOSITION
The most effective BPR teams include active representatives from the following work groups: top management, the business area responsible for the process being addressed, technology groups, finance, and members of all ultimate process users' groups. Team members who are selected from each work group within the organization will affect the outcome of the re-engineered process according to their desired requirements. The BPR team should be mixed in-depth and knowledge. For example, it may include members with the following characteristics:
• Members who do not know the process at all.
• Members who know the process inside-out.
• Customers and Suppliers.
• Members representing affected departments.
• One or two members of the best, brightest, passionate, and committed technology experts.
• Members from outside of the organization.
BUSINESS NEEEDS ANALYSIS
Another important factor in the success of any BPR effort is performing a thorough business needs analysis. In this analysis phase, a series of sessions to be held with process owners and stakeholders, regarding the need and strategy for BPR.
These sessions build a consensus as to the vision of the ideal business process. They help identify essential goals for BPR within each department and then collectively define objectives for how the project will affect each work group or department on an individual basis and the business organization as a whole. It is important to acknowledge and evaluate all ideas in order to make all participants feel that they are a part of this important and crucial process. The results of these meetings will help formulate the basic plan for the project.
This plan includes the following:
• identifying specific problem areas,
• solidifying particular goals, and
• defining business objectives.
ADEQUATE IT INFRASTRUCTURE
• Effective alignment of IT infrastructure and BPR strategy,
• Building an effective IT infrastructure,
• adequate IT infrastructure investment decision,
• adequate measurement of IT infrastructure effectiveness,
• proper information systems (IS) integration,
• effective re engineering of legacy IS,
• increasing IT function competency, and
• effective use of software tools is the most important factor that contributes to the success of BPR projects.
